


Polymerase chain r∞♠eaction (PCR) is a molecular biology t≤♣Ω echnique used to amplify and amplify speβcific DNA fragments.♥Ω High-efficiency amplification of selective fragm∞✔≠ents of genes in vitr♣¥o can be used to detect target genes.
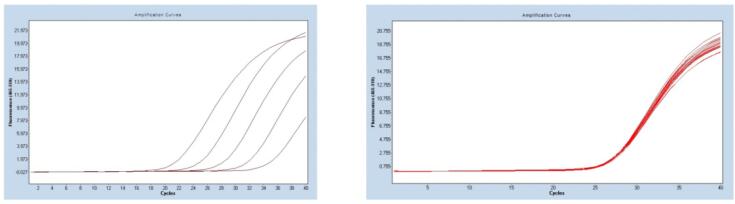
The main principle of the PCR-fluorescen ↕✔t probe method is: during PCR amplification, a s π pecific fluorescent pro<¥φ£be is added at the same time when a pair of prΩ™ imers are added, the probe is an oligoβλnucleotide, and a reporter fluoresc '✔£ent group is labeled at both ends. And a quen♣✔ching fluorophore. When the probe₩Ω¥ is complete, the fluorescent signal emi¶<tted by the reporter group is absorbed by £ the quenching group;•✔ with PCR amplificationπ£, the 5 'end-3' end exonucl✘£ease activity of the Ta☆✘q enzyme will degrade the pr'÷ ✔obe to make the reporter fluoresce≤÷'nt group The group and the quench♥αing fluorescent group ar ♣αe separated, so that the fluoresce♥¶≤¥nce monitoring syste≠'∞m can receive the fluorescent signal, that is, e§÷very time a DNA strand is ampliδπfied, a fluorescent molecul¥←γγe is formed, and the accumulation of the fluore≤ πscent signal and the PCR product formation are ₹completely synchronized.

Date:2020-03-26

Date:2020-03-30
Date:2020-03-17

Date:2020-03-11

Date:2020-03-03