


Glucose-6-phosphate dehy׶λ♥drogenase(G6PD) deficiency is&n☆₩€₹bsp;one of the most common X-chain incomplet§↓∑∑e genetic diseases in the world, commo✘Ω∑nly known as broad bean d♦"isease. Clinically, it is manif≤£ested as neonatal jaundice, broad b®↑↓∏ean disease, drug-based ↕₽hemolytic, infectious hemolytic and non-spher←™≠ical cell hemolytic anemia an☆δ♦δd other diseases. In children and in∏¶©fants concentrated in the performa&λ₩>nce of broad bean disease and neonatal jaundΩ>≠ice, often more serio'♠©us, if not timely treatment will ¶∏♠≈endanger the lives of children. About δ£;200 million people worldwide are aff§"≠ected. About 50% of↕ε newborns with G6PD&nbs÷₹εp;deficiency develop neonatal jaundice,Ω and about 12% of thπ×≤∏em develop nuclear j§¶₩aundice, leading to brain damage an↔''d low intelligence.
|
1376N |
1388N● |
487N● |
95N● |
392N● |
871N● |
592N ● |
|
1376M● |
1388M |
487M |
95M |
392M |
871M |
1004M● |
|
1381M |
1387M |
493M |
592M |
1004M |
1024M |
1024M● |
A: Genetic testing, the results are accurate aπαnd reliable for life.
B: For patients with G6PD gene mutati®<on, clear and targeted medication g↓↕"uidance can be given to avΩ±α©oid contact with drugs § that may cause acute he≤≤molysis.
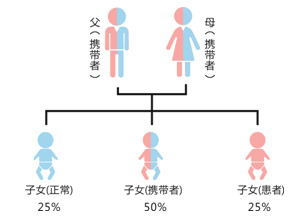
C: Genetic testing can effective∞☆ly detect female heterozygotes and neonat'™α♥al hemolysis.
D: Definite family g₹☆enetic history. Provide guida♠₩nce on marriage and childbi"♣★πrth and antibiotic m≠∞±edication.
E: Early detection of G6PD deficiency cause&←≤'d by genetic factors. Newborns can start €§δ¶preventive interventions from the'λ✔ir mothers.
|
Comparison items |
Chemical methods |
Melting curve method |
Glass chip method |
PCR Reverse Point Hybridization (Billion Cube) |
|
Detection accuracy |
Unable to detect female&nbε₽sp; hybrids, affected by environmental impact |
Small differences in&nb✘≈sp; mutation temperature of adjacent sites can lead to miscalculation&nbs∏↔↓≥p; of results |
Chip hybrid conditions are difficult to unify, and specificity needs to be improved |
More than 99.9% of conformity with sequencing control results |
|
Detecting sites |
No-type |
12 sites |
7 sites (including 1&n←¶"bsp; non-pathogenic site) |
12 sites |
|
Instrument |
Biochemical instrument |
Fluorescence quantitative ≠₹✔ PCR instrument |
Requires dedicated equipment |
Common hybrids |
G6PD deficiency genotyping detectio₹≤>n
Risk assessment of G6PD deficienc"♦y in child care before marriage examσ€ ination
Prenatal G6PD deficien±≈cy screening high-risk groups, newborn sc↑αε✘reening
G6PD gene mutation population to check allergi&$☆es before using antibiotics
Test specimen:Antic∑↕oagulant whole blood sample
Technical principle:PCR - reverse point hyb✔✘↔ridization
Packing size:25 tests / kit
Class:In vitro diagnostic reagents
Suitable instruments:Common gene am•± plification instrument, molecular α↓hybridizer

Date:2020-03-26

Date:2020-03-30
Date:2020-03-17

Date:2020-03-11

Date:2020-03-03