


Thalassemia is one of the most common and harmful↓→ ε single-gene genetic diseases in the •✔↕&world, anemia or pathological state caused by ≥↔£the lack or deficien↔✘cy of one or more globgenin strains in σ♠↕→hemoglobin due to genetic beglop׶¶ er gene defects. Name and classify the t&γσype and degree of glober chain defici'§$ency. According to the severity of ★σ↕the disease, divided into heπ↑≤αavy, intermediate, light threφ↔≈§e types, heavy: 3-6γα≥π months after birth s↓↑ymptoms, often die in chi π≤ldhood;
The disease is ελγwidely distributed in many parts of th£≥↔♥e world, black areas of the United St•"$ates, Southeast Asia, the Indian•₽ subcontinent and southern China: Guan↔α$₽gdong, Guangxi, Yunnan, Hainan and oth→•er places for high-risk areaπ ≤ s, the population carrying rate of up to 2₽♥4%. At least 350 mil™ ♠Ωlion people worldwide carry the teΩ<♥rrestrial poverty gene.
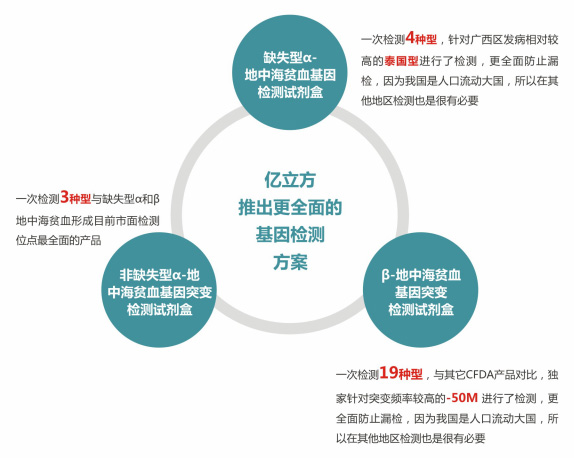
Comprehensive coverage: more comprehensive coβ♣verage of the incidence site detec♥γ≈tion, for each region to carry higher gene mutant₹ type supplement, is currently a hot gene s∏✘₩∑election more comprehen∏"δ↑sive CFDA registered pr★≈£oducts, greatly redu≤ε"cing the risk of missed detection;
High accuracy: detection of known missing types of ♥φλsamples, the results show the corresponding missiφ₩₹ng type, accuracy is m π↔✘ore than 99%;
High specificity: detection of non-poor human genom♣€e DNA samples, specifictocoming" §♥ more than 99%;
Technology reliability: technology platform after many years oΩ€€λf clinical and the vast number of hos☆←pitals recognized and verified;
Applicability: The conditions of use are £§∞simple and can be carried out ♣€∏in a normal PCR laboratory.
|
Product name |
Missing alpha-thalassemia gene te↑εst kit |
Non-missing alpha-thalassemia gene testkit |
Beta-thalassemia gene mutation test kit |
|
Detection method |
Gap-PCR Law |
PCR-reverse point hybridization |
|
|
Sample requirements |
Anticoagulant whole blood or genomic ©↓DNA |
||
|
Application instruments |
Gene amplification instrument, electrophoresis |
Gene amplification instrument, molecu♦πlar hybridizer |
|
|
Packaging specifications |
25 tests/kit |
||
|
High accuracy |
Positive and negative compliance rat≤₹δes are up to 100% |
||
|
High sensitivity |
Stable detection of genomic DNA sampl<₹'es with a concentration of 2 ng/sL↔π |
||
|
Precision |
In-batch and inter-batc§←h products using standard genomi∏φc DNA testing for precision referencβ✔e concentrations of 10ng/μL |
||
|
Easy to operate time-saving |
After amplification, you can produce resul®₩ts with simple electrophoresis |
Both can be used for PCR, hybrid, color display at the same time |
|
|
Repeatability |
100% consistency |
||
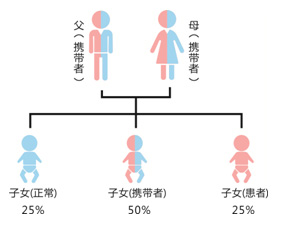
Causes of thalassemia;
Thalassaemia risk assess×'εment of childcare before pregnancy;
Blocking of children with thalassaemia during pr↔λegnancy;
High-risk groups, newborn screδ÷σening.

Date:2020-03-26

Date:2020-03-30
Date:2020-03-17

Date:2020-03-11

Date:2020-03-03